Restoring Old Batteries with Electrolyte Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
The lifespan of batteries is finite, and over time, their performance inevitably deteriorates. This decline is often attributed to the depletion or degradation of the electrolyte solution, a crucial component responsible for facilitating the flow of ions within the battery. While replacing old batteries is a common solution, restoring them with electrolyte solutions can be a viable option for extending their life and saving costs.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of restoring old batteries using electrolyte solutions, covering essential information such as:
- Understanding battery chemistry and the role of electrolytes
- Identifying the appropriate electrolyte solution for your battery type
- Safe and effective methods for restoring battery electrolytes
- Factors to consider when deciding whether to restore or replace a battery
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about restoring your old batteries and potentially prolong their useful life.
Understanding Battery Chemistry and Electrolyte Solutions
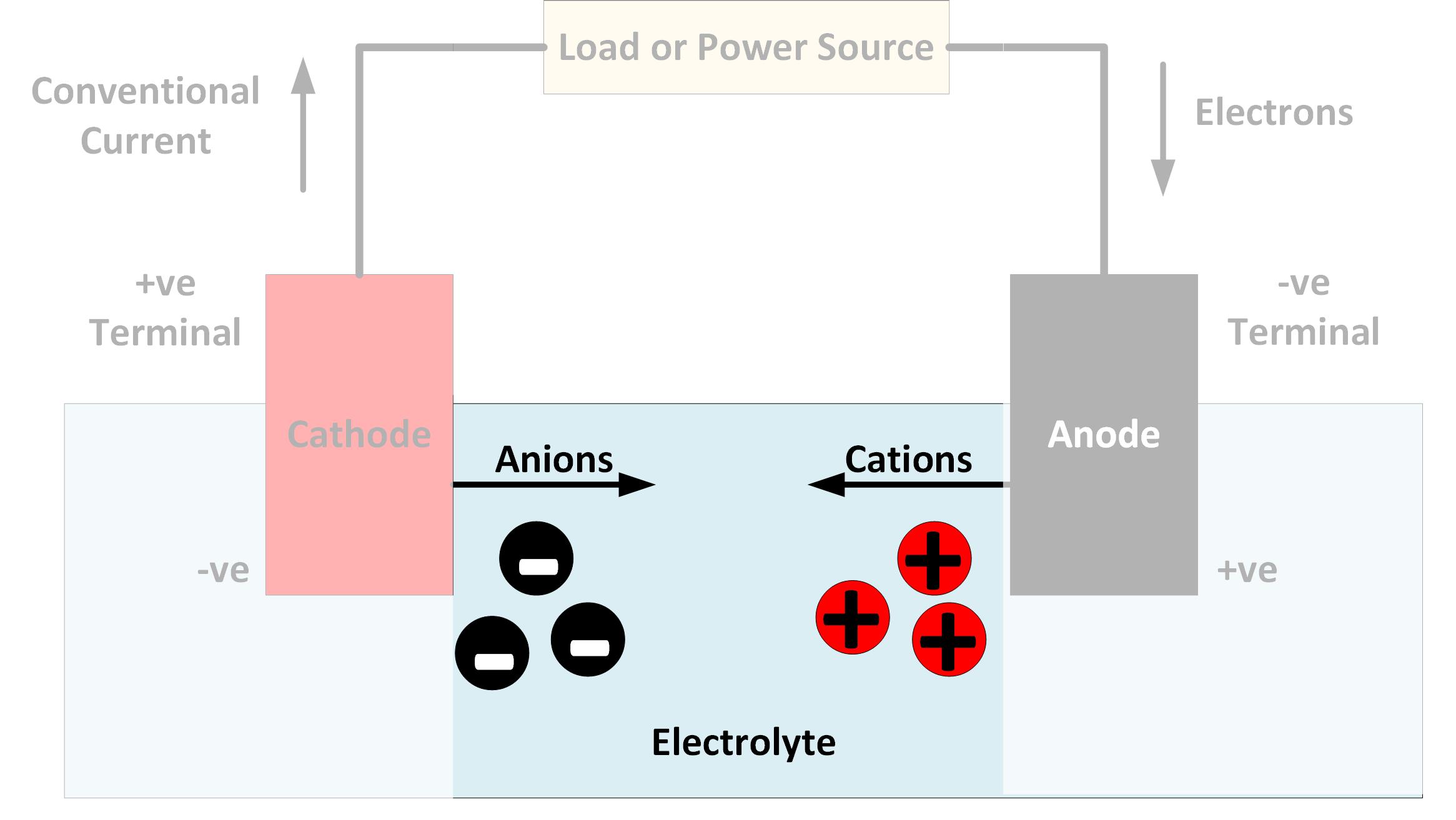
Batteries, regardless of their type, operate based on electrochemical reactions involving the movement of ions within an electrolyte solution. This solution acts as a conductor, enabling the transfer of electrical charge between the battery's electrodes (anode and cathode).
The specific type of electrolyte solution varies depending on the battery chemistry:
- Lead-acid batteries, commonly found in cars and motorcycles, utilize a sulfuric acid solution as their electrolyte.
- Lithium-ion batteries, prevalent in portable electronics, use a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent as the electrolyte.
- Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries employ a potassium hydroxide solution as their electrolyte.
Over time, electrolyte solutions can degrade due to factors such as:
- Evaporation: Electrolyte solutions can evaporate, leading to a reduction in their concentration and conductivity.
- Contamination: Impurities from the environment or internal battery components can contaminate the electrolyte, hindering its ability to conduct ions.
- Chemical reactions: Chemical reactions within the battery can consume or decompose the electrolyte solution, reducing its effectiveness.
Identifying the Appropriate Electrolyte Solution
Restoring a battery with electrolyte solutions necessitates using the correct type for the specific battery chemistry. Improper electrolyte use can result in irreversible damage, potentially rendering the battery unusable.
Always refer to the battery's specifications or consult a reliable resource to identify the appropriate electrolyte solution. For example, never use a sulfuric acid solution in a lithium-ion battery or vice versa. Doing so can lead to hazardous reactions and potentially cause a fire or explosion.
Methods for Restoring Battery Electrolytes
Restoring battery electrolytes involves replenishing or replacing the depleted or degraded solution. The specific methods employed vary depending on the battery type and the extent of its degradation.
Replenishing Electrolyte Solutions
For batteries experiencing a minor decrease in electrolyte level due to evaporation, replenishing the solution with distilled water can be sufficient. This method is commonly employed for lead-acid batteries.
To replenish the electrolyte:
- Disconnect the battery from any connected devices or circuits.
- Inspect the battery for any signs of damage or leaks. If any are present, do not attempt to replenish the electrolyte.
- Locate the fill caps on the battery's top. These caps are typically marked with "+" or "-" symbols corresponding to the battery's terminals.
- Carefully add distilled water to each cell until the electrolyte level reaches the recommended mark on the side of the battery.
- Reconnect the battery and charge it fully.
It is crucial to use only distilled water, as tap water contains impurities that can contaminate the electrolyte and damage the battery.
Replacing Electrolyte Solutions
In cases of significant electrolyte degradation or contamination, replacing the solution entirely might be necessary. This process is typically performed on lead-acid batteries and involves the following steps:
- Disconnect the battery and ensure it is fully discharged.
- Vent the battery to release any built-up pressure. This is usually achieved by opening the fill caps or using a specialized venting tool.
- Carefully drain the old electrolyte by siphoning or tilting the battery. Collect the old electrolyte in a designated container and dispose of it properly, following local regulations.
- Rinse the battery's cells with distilled water to remove any remaining electrolyte residues.
- Fill the battery cells with the appropriate new electrolyte solution, ensuring the level reaches the designated mark.
- Charge the battery fully before reconnecting it to the circuit.
Replacing electrolytes in lead-acid batteries should be performed with caution, as sulfuric acid is a corrosive substance. Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, eye protection, and a face mask.
Factors to Consider When Deciding Whether to Restore or Replace
While restoring battery electrolytes can extend their life, it is not always the most viable solution. Several factors need to be considered before deciding whether to restore or replace a battery.
Battery Age and Condition
Batteries that are very old or have suffered significant damage may not be suitable for restoration. The internal components, such as plates and separators, can deteriorate over time, rendering the battery irreparable. In such cases, replacement is the more sensible option.
Battery Type
Some battery types are more prone to electrolyte degradation and are generally easier to restore. For example, lead-acid batteries are relatively straightforward to restore compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Cost and Availability of Electrolyte Solutions
The cost and availability of appropriate electrolyte solutions for your battery type should be considered. If the cost of restoration is significantly high or if finding the correct electrolyte solution is challenging, replacing the battery might be a more cost-effective option.
Risk of Damage and Safety Concerns
Restoring battery electrolytes involves working with potentially hazardous substances, such as sulfuric acid. Improper handling or mishandling can lead to damage to the battery or personal injury. If you are not comfortable or equipped to handle these materials, replacement is the safer choice.
Conclusion
Restoring old batteries with electrolyte solutions can be a viable option for extending their life and saving costs. However, it is important to understand the battery chemistry, identify the appropriate electrolyte, and follow safe procedures. Consider the age, condition, type, and cost of the battery, as well as the associated safety risks, before deciding whether to restore or replace it. By making informed decisions and taking appropriate precautions, you can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your batteries.
0 Response to "How to Use Electrolyte Solutions to Restore Your Old Batteries"
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.